High-performance Homes in Arizona
Your trusted
high-performance
home experts in Arizona
What is a high performance home?
High-performance homes are becoming increasingly popular as homeowners prioritize energy efficiency, comfort, and cost savings over traditional home-building methods. With advances in technology and construction techniques, these homes are designed to save energy and money while providing maximum comfort.
High-performance homes are designed and built to be more energy efficient than traditional homes. They are constructed with better insulating materials and often include energy-saving features such as high-efficiency windows, doors, and appliances. They can also be equipped with special heating and cooling systems that reduce the energy needed to maintain a comfortable environment.
The Benefits of a High-Performance Home
The benefits of high-performance homes extend beyond energy savings. They tend to be more comfortable due to better insulation and air-sealing techniques. Additionally, high-performance homes can include photovoltaic panels, which generate electricity from the sun, and other renewable energy systems.
High-performance homes are often built with materials that enhance the environment’s health, such as formaldehyde-free insulation, which can reduce the risk of indoor air pollution. High-performance homes also bring additional financial benefits. By reducing the energy used to maintain a comfortable environment, homeowners can save money on their energy bills.
Net Zero or Near
Net Zero Energy
High-performance houses are built with energy efficiency in mind, using less energy for hot water production, heating, and cooling. They often feature photovoltaic solar panels that provide all of the home’s energy needs from renewable sources. As a result of the energy the house consumes, they have a carbon footprint that is either zero or almost zero.
High-performance homes often use batteries to store any extra renewable energy produced during the day for use at night. These residences often connect to the electrical grid via a net meter, also known as a bidirectional meter (this meter measures the flow of electricity in both directions), whether or not they have battery storage. This is important because solar panels on the house can provide more clean energy throughout the day than the home consumes.
Additionally, most energy-efficient homeowners enjoy lower utility costs because, in most regions, the power company gives the homeowner up to 100% credit for the surplus energy that the home’s solar panels generate.
Home Metrics for
High Performance
You may use metrics to evaluate the performance of high-performance houses. Here are a few examples:
HERS Index
The HERS (Home Energy Rating System) index is a way to measure the energy efficiency of a home. It calculates the amount of non-renewable energy a home uses, with a lower score indicating a more energy-efficient home. A score of 0 means that the home uses no net energy, while a score of 100 is the average for a new, conventional home. An older home is likely to score above 100, while a house with a negative HERS score produces more energy than it uses. For example, a home with a HERS score of -10 produces 10% more net energy than it consumes.
How energy-efficient a house is is determined by its airtightness, insulation, and an assortment of energy-efficient building systems, appliances, and other devices; this is also a factor in a home’s HERS score.
Installing PV solar panels can help improve a home’s HERS score by generating clean energy.
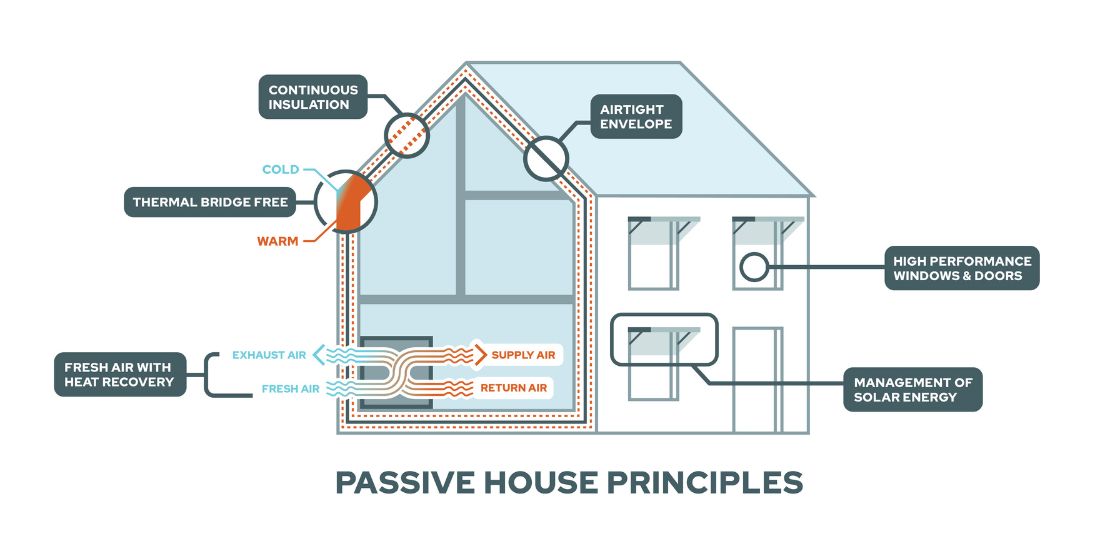
What Are Passive House Standards?
The Passive House standard is widely recognized as the most stringent energy-efficient building standard. A home built to this standard, without solar panels, typically has a HERS score between 37 and 40. As mentioned above, installing PV solar panels can decrease a home’s HERS score by generating clean energy. While it is possible for a conventional home or even an older home to achieve a HERS score of 0 by using solar panels, it may not meet all of the criteria to be considered a high-performance home.
To be considered a high-performance home, a building should not only have a low HERS score but also meet the requirements of standards such as LEED for Homes and the National Green Building Standards.
The ideal high-performance home would be energy-efficient, use solar panels, and have a HERS rating of 0 or lower.
Insulation
Proper insulation is essential for an energy-efficient home. The insulation required for a home to be considered high-performance may vary based on the climate zone and other factors.
Different parts of a home require different insulation measurement systems. The R-value measures the insulation for walls, floors, and attics, while windows are rated using a U factor. The R-value measures the level of insulation, with a higher R-value indicating a higher volume of insulation. High-performance homes typically have insulation with R-values that are higher than the minimum required by building codes for the specific climate zone.
The U factor measures the window’s ability to insulate the home, with a lower U factor indicating better insulation.
Indoor Air Quality
To meet the standards of a high-performance home, excellent indoor air quality (IAQ) is necessary. One way to ensure high IAQ is to follow the Indoor airPLUS green building certification standard, developed by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). This standard is often used when designing and building high-performance homes.
In addition to following specific guidelines, high-performance homes typically use a combination of approaches to achieve high IAQ. These approaches include the use of mechanical ventilation systems, the use of low-emitting materials, and the proper sealing and insulation of the home to prevent drafts and leaks. These approaches work together to create a healthy and comfortable indoor environment.

Building Materials Matter
If you want excellent indoor air quality, it is essential to use building materials that do not release harmful gases into the air. Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) are a class of gases of particular concern. Many products used in construction, such as paints, finishes, and adhesives, can emit VOCs when they are first used and continue to emit harmful gases over time. A home must be built using materials that emit low or no VOCs to be considered high-performance. This helps to ensure that the indoor air is safe and healthy to breathe.
Stale Air Out, Fresh Air In
There are three main ways that fresh air can enter a conventional home: through open windows or doors or gaps in the walls, attic, and roof. However, the air coming through these gaps is often contaminated with dust, insulation, and even pests and their droppings. In addition, conventional homes are not airtight, so a strong wind or negative air pressure caused by warm air rising in the house during the winter can push outside air through the walls. This can be harmful to people with certain medical conditions and is not energy-efficient.
In contrast, high-performance homes are designed to be virtually airtight so that no air can come in through the walls, attic, or windows. Instead, these homes use fresh air ventilation systems, such as Energy Recovery Ventilation (ERV) or Heat Recovery Ventilation (HRV) systems, to bring fresh air through dedicated air ducts.
These systems expel stale air from inside the home at a controlled rate and use recovered energy to preheat or cool the incoming fresh air. They also typically have a filter that prefilters the fresh air coming from outside, but there are other air filtration systems in a high-performance home. And, of course, you can still open the windows of your high-performance home for air if you like.
How Your Home's Air Is Filtered
To be considered a high-performance home, a building must also have a high-performance air filtration system, which is typically more effective than those used in conventional homes. These systems use MERV 13 filters or higher, which are rated based on their ability to filter out particles from the air.
MERV stands for Minimum Efficiency Reporting Values and is a scale that ranges from 1 to 20, with higher numbers indicating a greater ability to filter out particles. MERV 13 filters effectively remove particles larger than 1 micron and do a relatively good job of filtering out smaller particles between 1 and 0.3 microns.
Higher-numbered MERV filters, such as those ranging from MERV 14 to 20, can effectively filter out even smaller particles.
It is vital to have an effective air filtration system in place, as breathing in particle pollution can negatively affect health, particularly for those with respiratory issues. Fine particles, known as PM2.5, are particularly dangerous as they can reach the deep parts of the lungs or even enter the bloodstream.
Maximize energy efficiency
A green home should be designed to be as energy-efficient as possible. This means using energy-efficient appliances, installing energy-efficient lighting, using higher-grade insulation and weather-stripping to reduce air leakage, and using windows with a low thermal transmittance (U-value) to maximize indoor temperature control.
Choose green building techniques
Building techniques such as green roofs, also known as living roofs, and passive solar designs are options when building a green home.
At 928 Construction, our mission is to help our clients build the sustainable green home of their dreams. Our experts are ready to build from scratch.
Energy Recovery &
Air Tightness
A home’s airtightness, measured in air changes per hour (ACH), measures how much air can enter or escape a home when mechanical ventilation is not in use. A typical conventional home may have an ACH of 5 to 8, while older homes may have higher ACHs. New homes generally have an ACH of 5. In contrast, a certified Zero Energy Ready Home (a high-performance home standard) has an ACH of around two or lower, and a certified Passive House has an ACH of about 0.5.
High-performance homes often use Heat Recovery Ventilation (HRV) or Energy Recovery Ventilation (ERV) systems to achieve a high level of airtightness and maintain good indoor air quality. These systems recover a significant portion of the energy used to heat or cool the home while providing proper ventilation with fresh air. These systems typically recover 80-95% of the energy used to heat or cool the home, making the home highly energy-efficient and therefore considered high-performance.

